Home» Pharmaceutical Analysis» Sterilization Residues Analysis
Sterilization Residues Analysis
Ethylene oxide gas, also known as EtO or EO, is the most commonly used sterilization gas for pharmaceutical vessels, injectable vials / containers, sterile products and medical devices. Ethylene oxide has low boiling point of 10.7 oC. It is in gas form at room temperature and can diffuse well into complex surfaces and devices, making it a preferred route of sterilization. However, it can lead to residual gases and degradation byproducts such as Ethylene Chlorhydrin (ECH) & Ethylene Glycol (EG).
Ethylene oxide is also used as a base product for a variety of pharmaceutical and industrial base products such as PEG, Polyurethanes, Alkyl Alkanolamines, Choline Chloride, Ethanolamines, Ethyleneamines, Glycol Ethers, Glycol Ethers Acetates, Solvents etc. And therefore, residual Eto and its byproducts are of concern to human health.
EtO Toxicity
Ethylene Chlorohydrin Toxicity
CLL’s Services for Sterilization Gas Residues Monitoring & Testing
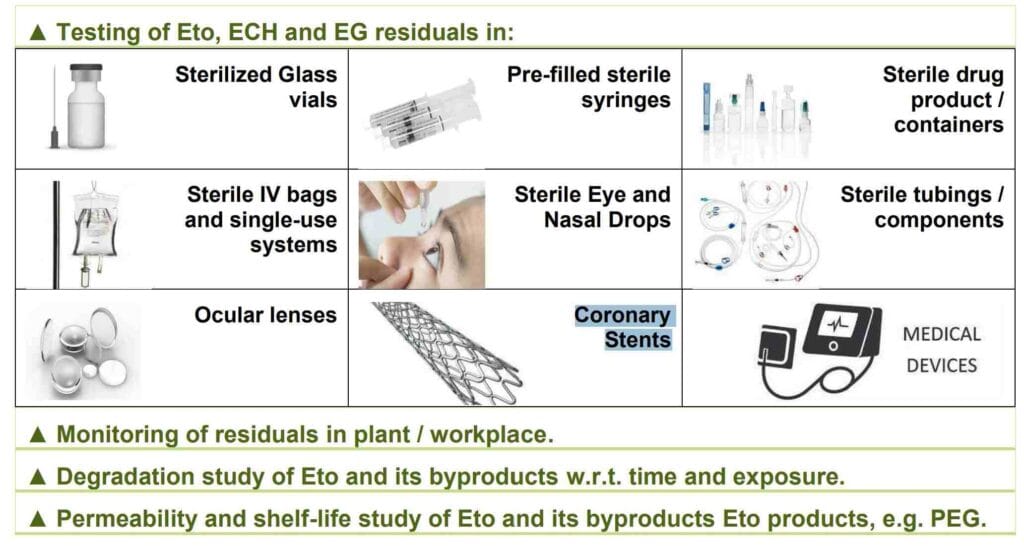
| ▲ Testing of Eto, ECH and EG residuals in: | ||
| Sterilized Glass vials | Pre-filled sterile syringes | Sterile drug product / containers |
| Sterile IV bags and single-use systems | Sterile Eye and Nasal Drops | Sterile Eye and Nasal Drops |
| Ocular lenses | Coronary Stents | Medical Devices |
| ▲ Monitoring of residuals in plant / workplace | ||
| ▲ Degradation study of Eto and its byproducts w.r.t. time and exposure. | ||
| ▲ Permeability and shelf-life study of EtO and its byproducts EtO products, e.g. PEG | ||
Methods
Regulatory References
The limits of Ethylene oxide and its byproduct Ethylene Chlorohydrin have been defined as follows, where ICH M7 limits are not applicable:
Analyte | Raw Materials | Finished Products | Containers |
Ethylene oxide | 1 μg/g | 1 μg/g | 1 μg/mL |
Ethylene Chlorohydrin (or any other halogenated ethylenehydrine) | 50 μg/g | 50 μg/g | 50 μg/mL |
ISO 10993 for Medical Devices: has defined EtO exposure as follows:
Analyte | Permanent Contact Devices | Prolonged Exposure Devices | Limited Exposure Devices |
Ethylene oxide | 24 hours: <4 mg 30 days: <60 mg | 24 hours: <4 mg 30 days: <60 mg | < 4 mg |
Ethylene Chlorhydrin (or any other halogenated ethylenehydrine) | 24 hours: <9 mg 30 days: <60 mg | 24 hours: <9 mg 30 days: <60 mg | < 9 mg |
ISO 10993 for Medical Devices for special cases
Medical Device | Residue of EtO | Residue of ECH |
Intraocular lenses | Not to exceed 0.5 µg EO per lens per day, or, 1.25 µg per lens | NA |
Blood cell separators | 10 mg | 22 mg |
Blood oxygenators and blood separators | 60 mg | 45mg |
Devices used in cardiopulmonary bypass procedures | 20mg | 9mg |
Extracorporeal blood purification devices | 4,6 mg/device | 4,6 mg/device |
Drapes that are intended to contact only intact skin | TCL = 10 µg/cm2 | TCL = 5 mg/cm2 |
Note: TCL = Tolerable Contact Limit
Workplace Exposure limit for Ethylene Oxide
OSHA (Occupational Safety & Health Administration, USA) Airborne (Workplace) Exposure limit for Ethylene oxide is 1 ppm (for an 8-hours work shift) with a maximum excursion of 5ppm for 15minutes.
Turnaround Time
- Quality Control Analysis: 5 – 10 business days (Rush services available)
- Workplace monitoring: 5 – 10 business days (Rush services available)
- Analytical Method development and validation: 3 to 4 weeks.
