Home» Pharmaceutical Analysis» Pharmaceutical Package Performance Testing
Pharmaceutical Package Performance Testing
Why is shipping containers performance testing required?
After spending billions of dollars on product research, and setting up a near flawless manufacturing set-up, one may have a perfect product. However, if the right packaging container is not qualified, the end-product with the customer may be less than satisfactory. Worse still, in case of sterile products, it may cause harm to the end- consumer.
Drug product shipping containers / packages must be able to protect the drug product’s integrity; in case of medical devices, the shipping container / package must be able to protect the sterility, performance and function.

Are there any international guidelines for this?
There are several guidelines that are available such as ASTM and ISTA. We follow the US-FDA recognized ASTM D4169 which is considered the gold standard.
EU Legislation Guidelines of 5 November 2013 on Good Distribution Practice of medicinal products for human use (Text with EEA relevance) (2013/C 343/01), also state:
“9.3. Containers, packaging and labelling Medicinal products should be transported in containers that have no adverse effect on the quality of the products, and that offer adequate protection from external influences, including contamination. C 343/10 Official Journal of the European Union 23.11.2013 EN Selection of a container and packaging should be based on the storage and transportation requirements of the medicinal products; the space required for the amount of medicines; the anticipated external temperature extremes; the estimated maximum time for transportation including transit storage at customs; the qualification status of the packaging and the validation status of the shipping containers.”
FDA 483s on Shipping Distribution Studies:
Failure to ensure that device packaging and shipping containers are designed and constructed to protect the device from alteration or damage during the customary conditions of processing, storage, handling and distribution, as required by 21 CFR 820.130.
For example, your firm has not adequately demonstrated that the terminally sterile medical packaging and product can withstand the rigors of transit, handling, storage environments without compromising the sterility of the pack, product features and performance.
What tests are carried out for performance testing of packaging containers?
Some of the tests that are carried out for performance testing of pharmaceutical packages are:
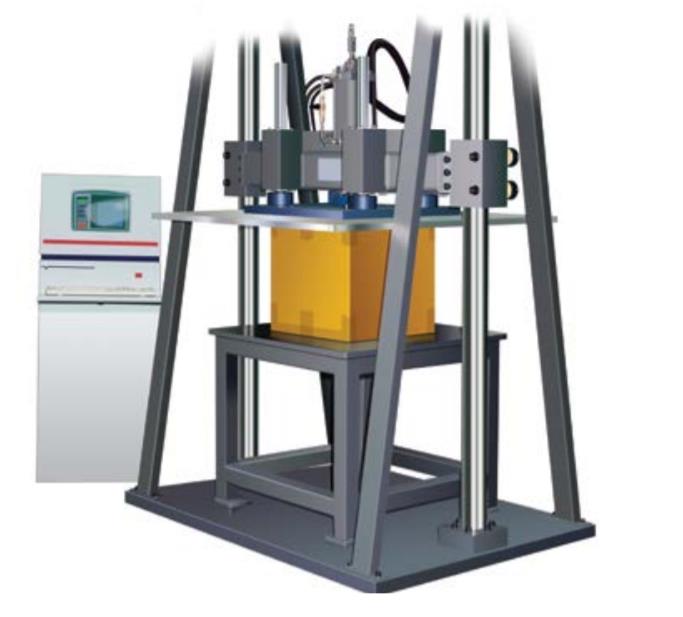
ASTM D 642 Compressive Resistance to check for stacking (load bearing) capacity during transit.
ASTM D 880 Impact Testing for Shipping Containers and Systems to check for impact on package as well as contents due to sudden forces during transit.
ASTM D 951 Test Method for Water Resistance of Shipping Containers to check for water absorption /repellency by package by water spray method during transit.
ASTM D 999 Test Methods for Vibration Testing of Shipping Containers (to simulate impact of vibrations on package and contents during road and airline transit).
ASTM D 5276 Test Method for Drop Test of Loaded Containers by Free Fall (to simulate impact of sudden drop / fall during handling in warehouse or during loading/unloading).

ASTM D 5487 Test Method for Simulated Drop of Loaded Containers by Shock Machines. (to simulate impact of sudden drop / fall during handling in warehouse or during loading/unloading).
ASTM D 6055 Test Methods for Mechanical Handling of Unitized Loads and Large Shipping Cases and Crates.

How is simulated shipping distribution study carried out?
The ability of the shipping units to withstand the distribution environment is verified by subjecting them to a test plan consisting of a sequence of anticipated hazard elements encountered in various distribution cycles. So for example, if the end-product were to be packed in a corrugated box, stacked in a warehouse for storage, shipped by cold storage truck, transported by airplane and then again by truck to the final destination, the same distribution cycle would be simulated in the laboratory to establish if the distribution package and the cycle impact the quality of end-product in any way.
Shipping Distribution Study Protocol
CLL has developed a 4-step path for simulated distribution study protocols:
Step 1
Selection of package types.
Step 2
Establishing shipping distribution paths andidentifying the worst-case scenario. Establishing end- points and acceptancecriteria.
Step 3
Determination of analytical study end-units(pre-filled packaging container).
Step 4
Evaluating and selection of shipping packages / containers based on final performance report.
Where do we carry out performance tests and simulated distribution studies?
From simple over-the-counter (OTC) products to prescription drugs such as tablets, capsules, topical creams and liquids to sophisticated drug delivery devices, packaging performance testing and simulated distribution studies can help manufacturers’ get an understanding of how their end-product will fare at the end of their distribution cycle.
CLL can develop protocols in collaboration with clients and determine acceptable end-points. Determination of the optimal packaging will provide several cost benefits as well as a reduction in market complaints due to broken/ damaged drug product container / devices.
Our cGMP and ISO 17025 accredited laboratories provide complete container as well as shipping studies platform.
Containers Testing
Our Container Testing laboratory offers comprehensive qualification testing for all primary container components – plastics, glass and elastomeric closures. Our cGMP laboratory can assist with all testing required for regulatory compliance to USP, EP and JP standards for Container Permeation Testing, Material Identification Testing, Extractable Testing and Functionality Testing.
Container Closures Moisture Barrier Properties
Our Laboratories offer facilities to determine adsorption (MVTR), Water Vapor Transmission Rate (WVTR) via USP <671> for container closures. These barrier properties tests help you plan the optimal packaging material choice for specific applications to maximize preservation and prolong the shelf life of your product.

